How to Upscale Lossy MP3 Files into High-Quality WAV Files
If you've ever tried to convert an MP3 back to WAV, you already know the truth: the quality doesn't magically improve. The file size gets bigger, but the sound stays exactly the same. That's because MP3 compression permanently removes audio information to save space. You cannot reverse this process with traditional tools.
But what if you could rebuild what was lost? Modern AI audio restoration services like Neural Analog don't just stretch your audio files. They actually reconstruct missing frequencies, remove compression artifacts, and restore the natural harmonic content that makes music feel alive. Think of it as the difference between resizing a pixelated photo and using AI to fill in the missing details.
In this guide, you'll learn why simple conversion fails, how neural restoration works, and when to use it to truly improve your music quality.
Why Converting MP3 to WAV Fails: The Data Is Gone
MP3 compression works by throwing away what it thinks you won't notice. It reduces dynamic range, adds quantization noise, and cuts frequencies based on the bitrate. A 128 kbps MP3 typically cuts everything above 16 kHz . Even a 320 kbps MP3 can cut frequencies above 20.5 kHz depending on the encoder settings . The result is lost harmonic detail and added artifacts.
When you convert MP3 to WAV in Audacity or iTunes, you're doing interpolation. This is mathematical curve fitting that stretches existing data across a larger canvas. It does not add detail. It cannot bring back what was deleted. The spectrogram shows the same dark void in the high end, just with more empty pixels.
This is why professionals always keep lossless masters. Once you go lossy, you cannot go back without help.
Understanding Audio Quality: The Specs That Actually Matter
Before we talk about restoration, you need to understand what defines audio quality. These concepts explain why restored files sound better.
Sampling Rate: 44.1 kHz vs 48 kHz
44.1 kHz (44,100 samples per second) is the CD standard. It captures frequencies up to 22.05 kHz, which exceeds human hearing (20 kHz). 48 kHz is common in video production, offering slightly more headroom.
Most streaming platforms use 44.1 kHz, but compress it heavily. When you upscale an MP3, restoring to 44.1 kHz is standard. Neural Analog specifically restores audio to 44.1 kHz WAV, extending frequency response up to 20 kHz to recover the full audible spectrum.
Bit Depth: 16-bit vs 24-bit WAV
Bit depth determines dynamic range, which is the difference between the quietest and loudest sounds.
- 16-bit: 96 dB dynamic range. Good for final distribution (CDs, streaming)
- 24-bit: 144 dB dynamic range. Essential for production, mixing, and restoration
A 16-bit file that is quiet then loud can have quantization noise. 24-bit provides headroom to push levels without distortion.
High Frequencies Spectrum Recovery: Why 20 kHz Matters
Most audio devices can generate sound from 20Hz to 20Khz. That's because humans can hear up to 20 kHz when young. This usually drops to 16-18 kHz with age and, unfortunately, the exposition to loud sound environments (cars, machinery, concerts, radio in restaurants...).
You also need to know that humans don't perceive all frequencies as equally loud: frequencies close to human voice will feel "louder", despite the audio signal intensity being the same.
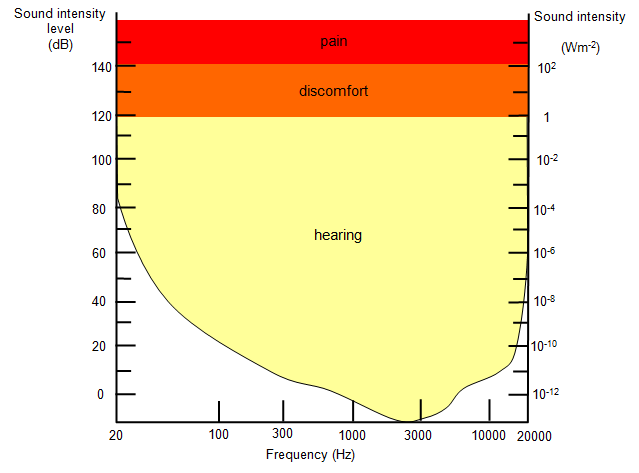
Let's be real: you'd have to be a bat to listen only to music made up of ultrasounds above 15Khz. However, high frequencies still affect spatial feel and transient response. Cymbals, string shimmer, and vocal air live in this range. Moreover, high frequencies impact the audio effect algorithms, such as compression, limiters, EQ, or reverb.
MP3 cuts this severely, especially at lower bitrates. Spectrum recovery rebuilds these frequencies based on learned patterns. Even if you cannot hear a pure 18 kHz tone, you perceive the restored "air" and "space." This is why restored tracks sound wider and more open.
Streaming Platform Audio Quality: The Hidden Problem
Spotify, Apple Music, and YouTube use lossy compression. Even their "high quality" settings discard data. AI music generators like Suno and Udio often output low bitrate MP3s because they were trained on compressed data.
This creates a quality ceiling. Your track might be brilliant, but it sounds muffled. Upscaling breaks through this ceiling by restoring pre-streaming quality.
How Neural Audio Restoration Actually Works
Modern AI doesn't guess. It learns. Here's the simplified process to explain how the Neural Analog restoration model works:
Learned Signal Statistics
The model trains on millions of song pairs: pristine studio masters and their MP3 versions. It learns what compression destroys and what natural music should look like. It understands that a guitar strum creates specific harmonics, that vocals have predictable formants, that drums need phase coherence.
Band-Split Reconstruction
The audio spectrum is divided into sub-bands. Low frequencies are preserved (they're usually clean), while mid and high bands are rebuilt using learned harmonic structure. This targeted approach avoids messing up the solid foundation while fixing what's broken.
Time-Domain Consistency
The model ensures that new details are phase-coherent. Added high frequencies align with the original waveform's timing. No weird flanging or smearing. The result sounds natural, not processed.
Optimized for Perception
Model's outputs are measured against objective quality metrics and human perception tests. The goal isn't just technical accuracy, it's musical fidelity. Clearer highs, tighter transients, larger soundstage.
Real Examples: Before and After Restoration
Most AI music generators produce 16 kHz MP3 files because their training data was compressed. The result sounds good but lacks professional sheen.
Neural Analog restores these to 20 kHz WAV. Listen to the difference which is noticeable in the high frequencies and in parts without drums. Pay attention to cymbals, reverb tails, and the digital chirps.
Restore missing high frequencies
Low sample rate musics, such as old recordings or AI generated tracks, miss high frequencies. Use Neural Analog to restore high frequencies.
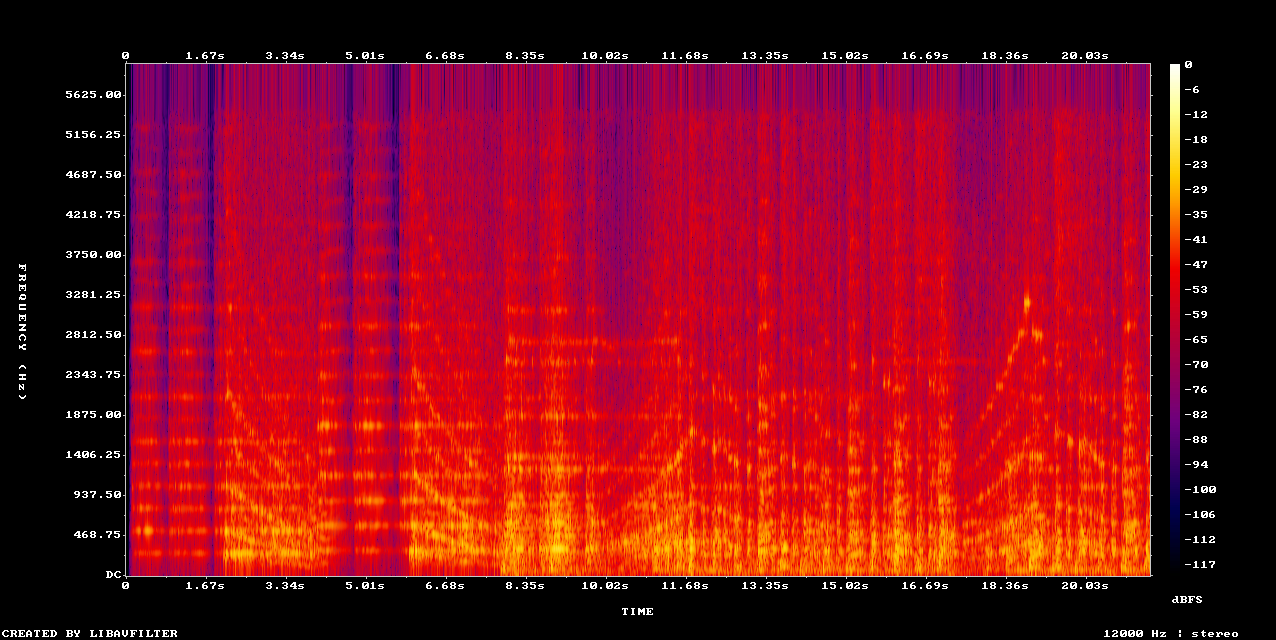
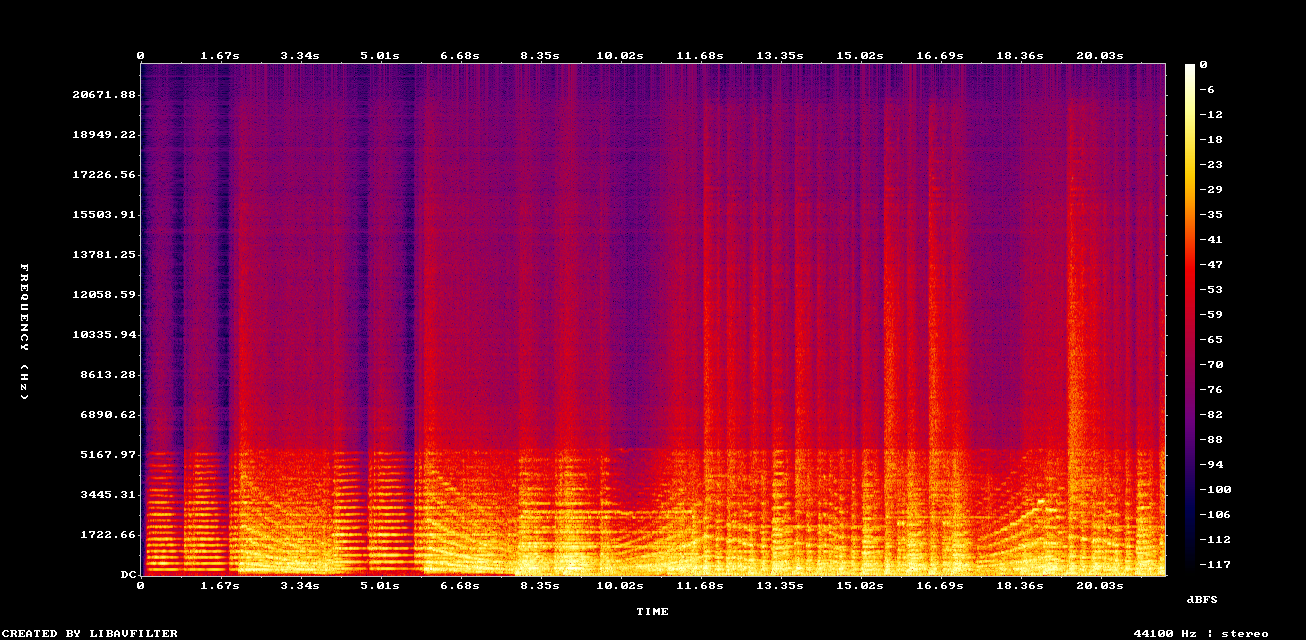
Example: Music Upscaler on low quality mp3 recording
Remove clipping from poor recordings
Clipping is what happens when the audio is too loud to be encoded. Use Neural Analog to remove clipping artifacts while maintaining high volume.
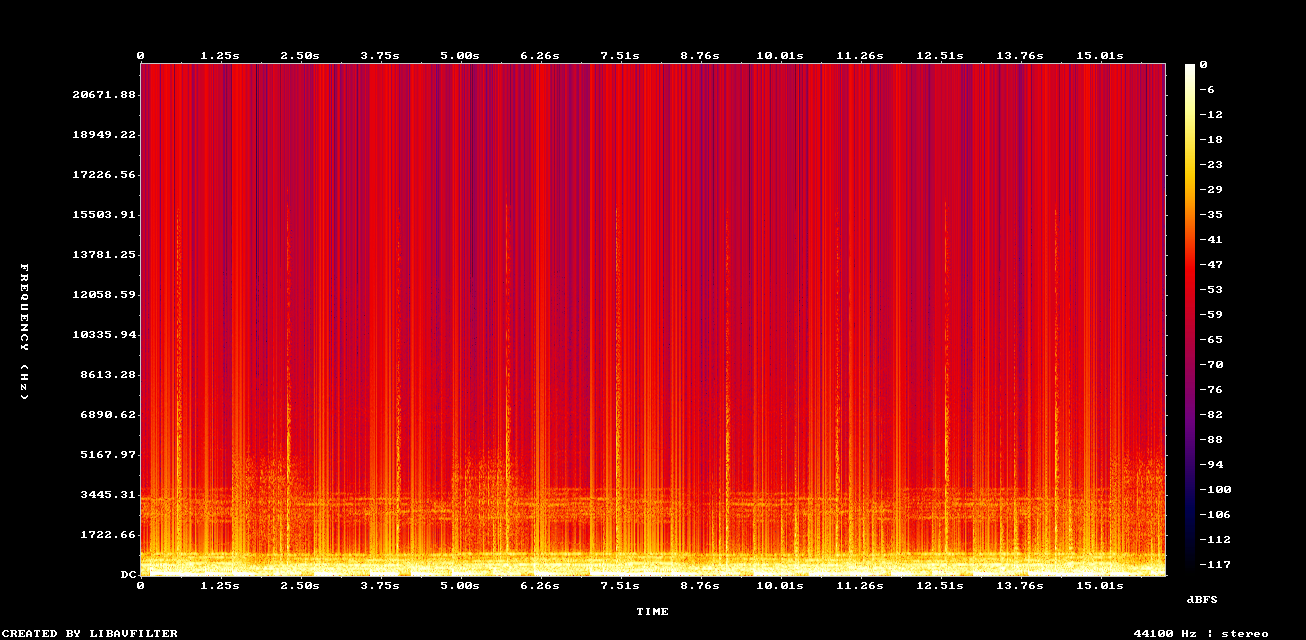
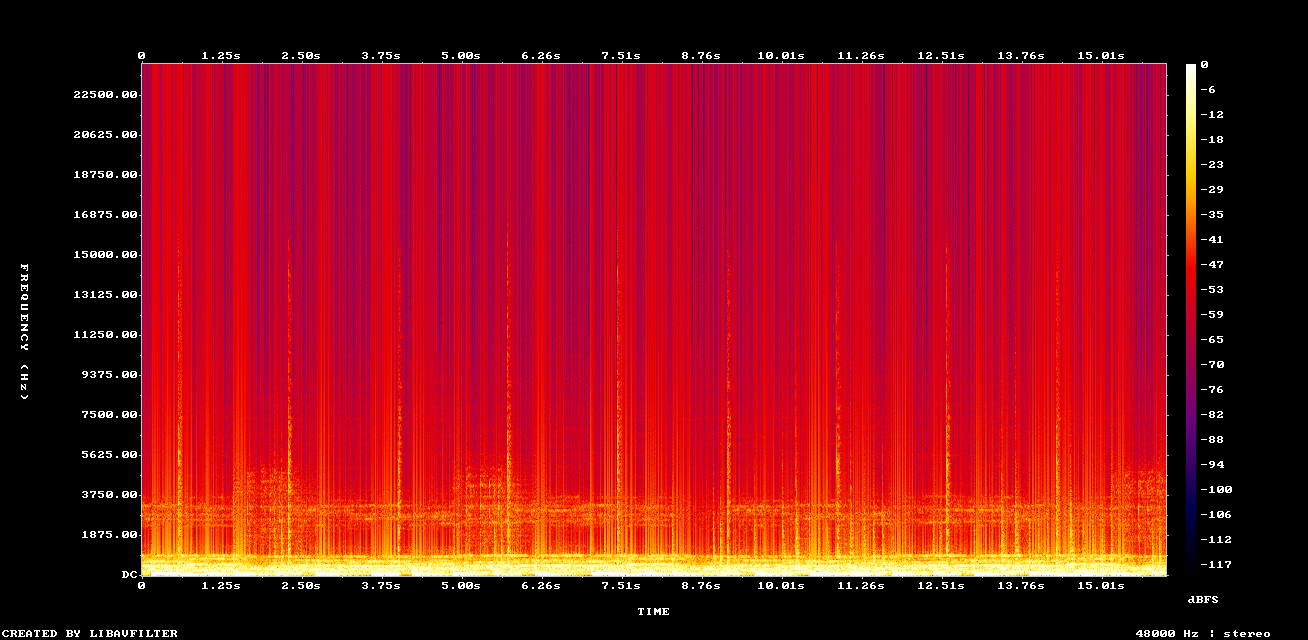
Example: Remove Clipping + DACVAE upscaling on old mp3 file
Upscale English speech audio quality
Use Neural Analog to upscale voice tracks, singing, and speech thanks to the NovaSR model.
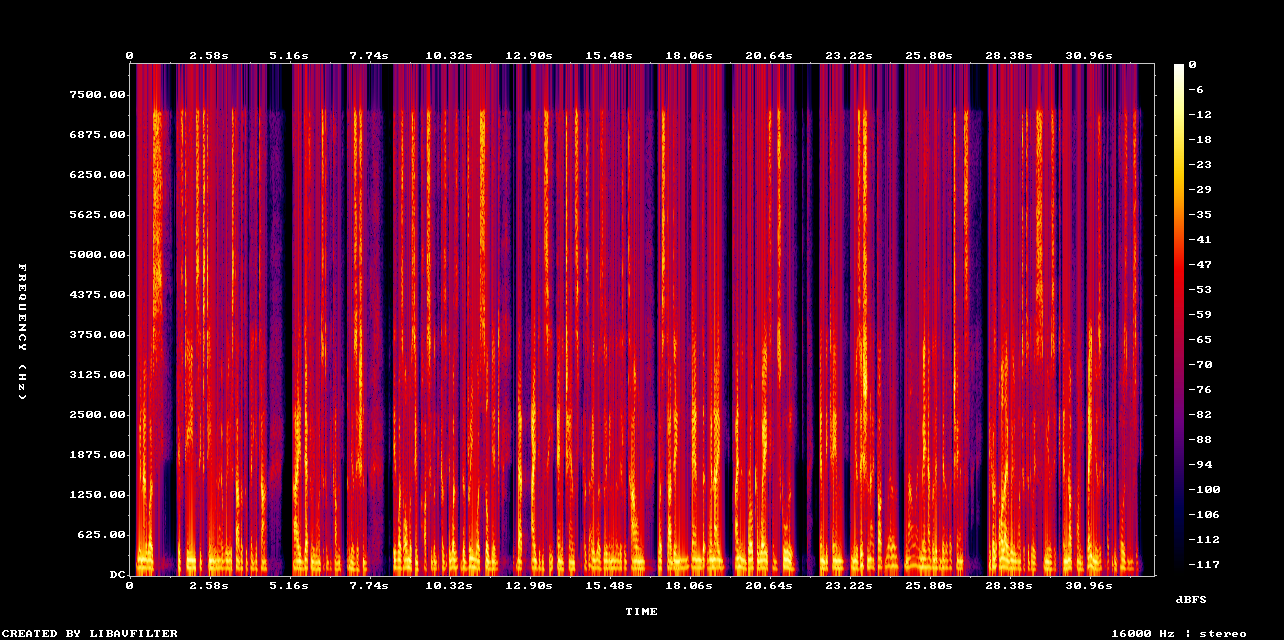
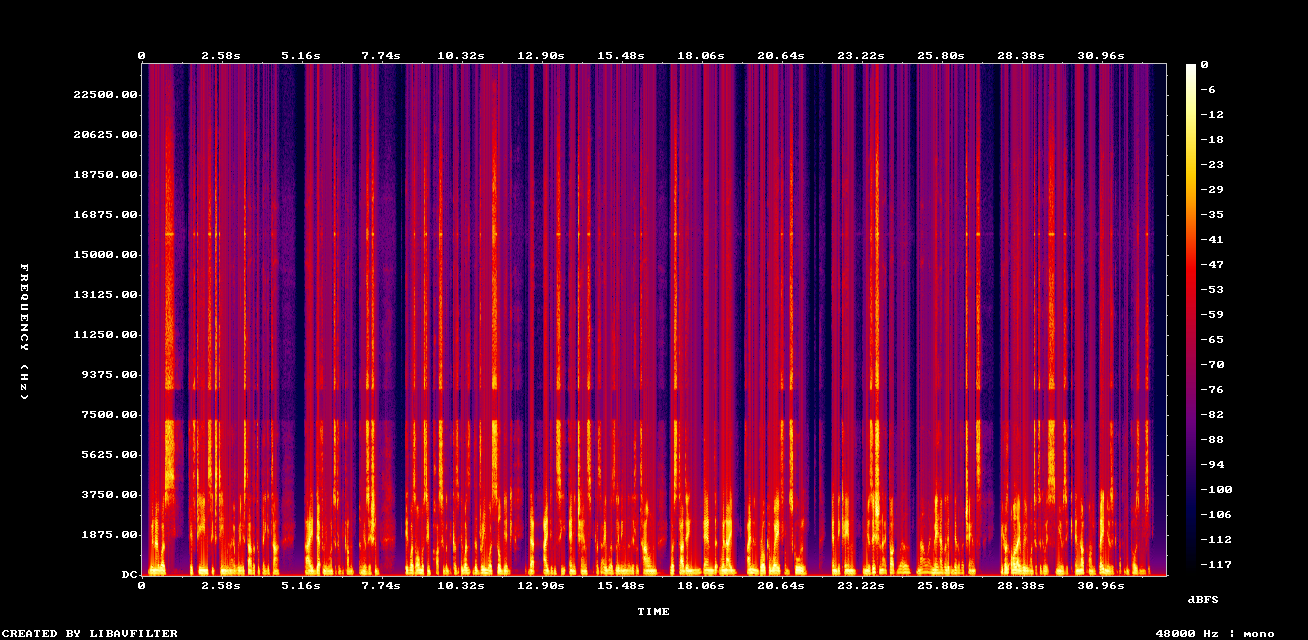
Example: Upscaled speech with NovaSR (mono)
When to Use Audio Upscaling: Clear Use Cases
Improve AI Music Quality
If you use Suno, Udio, or Producer.ai, you're starting with compressed audio. Upscale immediately after generation to maximize quality before mixing. This gives you better source material.
Convert to WAV Lossless from Streaming Downloads
Beatport, Bandcamp, and other stores sometimes sell MP3s due to licensing. Upscale these to WAV for sample extraction, remixing, or archival. The restored files are ready for serious production.
High Frequencies Spectrum Recovery for Remasters
Old MP3 libraries from the 2000s are full of 128 kbps files. Restore them to modern standards for playback on high-end systems. The difference on good headphones or studio monitors is dramatic.
Preparing Audio for Mastering
Never master an MP3. Always restore first. Mastering engineers need full-spectrum audio to work with. Sending them a restored WAV shows professionalism and respect for the craft.
How to Use Neural Analog: Three Simple Steps
You don't need to install Python, manage GPU drivers, or download gigabytes of models.
Step 1: Import Audio Upload your MP3 or paste a link from Suno, Udio, YouTube, or Producer.ai.
Step 2: Neural Reconstruction Click restore. The system processes your audio using generative AI trained on professional music. This takes seconds, not hours.
Step 3: Download WAV Get a 44.1 kHz WAV file with restored frequencies up to 20 kHz. Import it into your DAW and work with real quality.
No command line. No configuration. Just better audio.
Frequently Asked Questions
Are restored frequencies above 16 kHz actually audible?
Yes, depending on age and hearing health. For example, most teenagers can hear the 17.4Khz ultrasound called "Mosquitone".
But more importantly, they affect spatial perception and transient clarity. Even if you cannot hear a pure 18 kHz sine wave, you perceive the restored "air" and depth. This is why high-resolution audio feels more open.
What is the difference with simply converting to WAV in my DAW or in Audacity?
Converting to WAV is interpolation. It stretches existing data without adding detail. Neural Analog performs generative reconstruction, similar to how AI upscaling works for images. It predicts and inserts missing harmonic content.
Does the model just add noise?
No. Unlike enhancers that layer white noise to sound "fuller," neural restoration reconstructs coherent signal. The AI learns to distinguish between musical content and compression artifacts, removing the latter while rebuilding the former. You can see that by looking at the reconstructed spectrograms.
Can restoration fix my poorly mixed track?
No. Restoration removes artifacts and extends bandwidth. It cannot fix reverb balance, muddy bass, or clipping. That's mixing, not restoration. To address that, the process is usually to use Neural Analog's stem splitter and fix the mixing on each stem (instrument track).
Is restoration free?
Neural Analog lets you restore short samples free to test quality. For full tracks, you'll need a Pro subscription. This covers GPU processing costs and model maintenance.
What about 48 kHz vs 44.1 kHz?
Most AI generators and streaming platforms use 44.1 kHz. Neural Analog restores to this standard because it's what you'll release to. The difference between 44.1 kHz and 48 kHz is minor compared to the gap between compressed and restored audio. Focus on restoration quality, not minor sample rate differences.
Methodology Comparison: Choose the Right Tool
| Feature | Interpolation | Mastering (EQ/Comp) | Neural Analog Restoration |
|---|---|---|---|
| Method | Mathematical curve fitting | Frequency/dynamic adjustment | Generative AI reconstruction |
| Bandwidth Extension | No | No | Yes (restores 20 kHz) |
| Artifact Removal | No | Often makes worse | Yes (de-quantization) |
| Process | Upsampling | Polishing | Restoration |
| Best For | Quick format change | Final polish | Quality recovery |
Streaming Platform Audio Quality: The Bigger Picture
Spotify's "Very High" quality is 320 kbps Ogg Vorbis. Apple Music uses AAC at 256 kbps. Both are lossy. YouTube heavily compresses everything.
If you upload a restored WAV to these platforms, you start from the best possible source. The final stream will still be compressed, but it begins with full spectrum audio. This means better artifacts after platform compression, not worse.
For producers, this chain matters: Restore → Mix → Master → Distribute. Skipping restoration is like filming a movie with a dirty lens. You can color grade later, but the blur remains.
Don't Settle for Subpar Quality
MP3 was designed for dial-up internet and iPods with 5GB storage. We're in the era of unlimited bandwidth and studio-grade AI tools. There's no reason to work with compromised audio.
Neural Analog gives you professional restoration without the learning curve. Upload your MP3, download a WAV with frequencies restored to 20 kHz, and hear what you've been missing.
Your audience deserves full quality. Your tracks deserve full quality. Most importantly, your creative vision deserves to be heard as intended. Import your first track today.